Sublime Text 可视化编辑Markdown
Posted on 27 May 2014 MarkdownSublimeSoftware 添加评论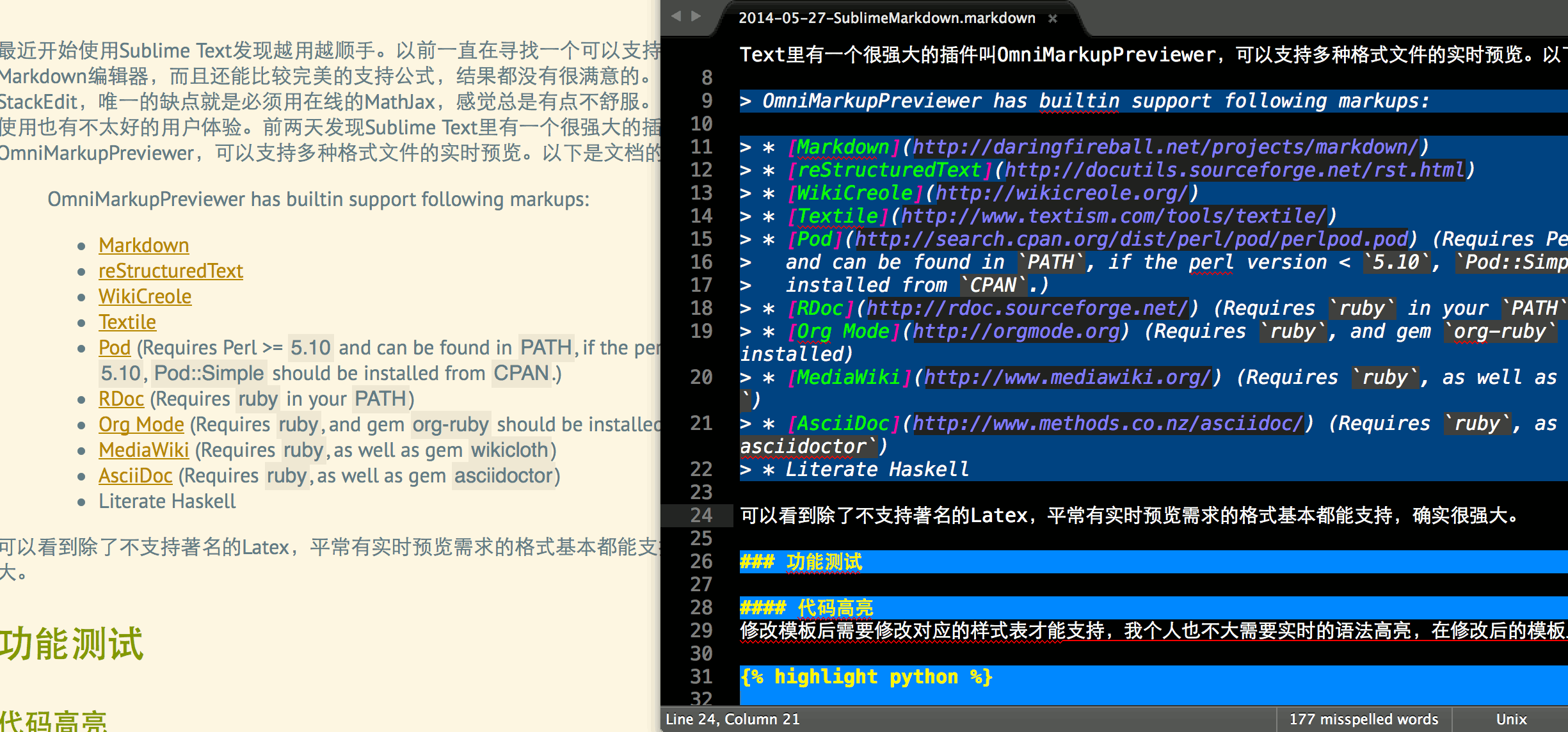 最近开始使用Sublime Text发现越用越顺手。以前一直在寻找一个可以支持离线实时预览的Markdown编辑器,而且还能比较完美的支持公式,结果都没有很满意的。后来就开始使用StackEdit,唯一的缺点就是必须用在线的MathJax,感觉总是有点不舒服。当然在浏览器里使用也有不太好的用户体验。前两天发现Sublime Text里有一个很强大的插件叫OmniMarkupPreviewer,可以支持多种格式文件的实时预览。以下是文档的摘要:
最近开始使用Sublime Text发现越用越顺手。以前一直在寻找一个可以支持离线实时预览的Markdown编辑器,而且还能比较完美的支持公式,结果都没有很满意的。后来就开始使用StackEdit,唯一的缺点就是必须用在线的MathJax,感觉总是有点不舒服。当然在浏览器里使用也有不太好的用户体验。前两天发现Sublime Text里有一个很强大的插件叫OmniMarkupPreviewer,可以支持多种格式文件的实时预览。以下是文档的摘要:
OmniMarkupPreviewer has builtin support following markups:
- Markdown
- reStructuredText
- WikiCreole
- Textile
- Pod (Requires Perl >=
5.10and can be found inPATH, if the perl version <5.10,Pod::Simpleshould be installed fromCPAN.)- RDoc (Requires
rubyin yourPATH)- Org Mode (Requires
ruby, and gemorg-rubyshould be installed)- MediaWiki (Requires
ruby, as well as gemwikicloth)- AsciiDoc (Requires
ruby, as well as gemasciidoctor)- Literate Haskell
可以看到除了不支持著名的Latex,平常有实时预览需求的格式基本都能支持,确实很强大。
功能测试
代码高亮
修改模板后需要修改对应的样式表才能支持,我个人也不大需要实时的语法高亮,在修改后的模板上就没有折腾了。
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Linear interpolation in N-D
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------
class LinearNDInterpolator(NDInterpolatorBase):
"""
LinearNDInterpolator(points, values, fill_value=np.nan)
Piecewise linear interpolant in N dimensions.
.. versionadded:: 0.9
Parameters
----------
points : ndarray of floats, shape (npoints, ndims); or Delaunay
Data point coordinates, or a precomputed Delaunay triangulation.
values : ndarray of float or complex, shape (npoints, ...)
Data values.
fill_value : float, optional
Value used to fill in for requested points outside of the
convex hull of the input points. If not provided, then
the default is ``nan``.
Notes
-----
The interpolant is constructed by triangulating the input data
with Qhull [1]_, and on each triangle performing linear
barycentric interpolation.
References
----------
.. [1] http://www.qhull.org/
"""
def __init__(self, points, values, fill_value=np.nan):
NDInterpolatorBase.__init__(self, points, values, fill_value=fill_value)
if self.tri is None:
self.tri = qhull.Delaunay(self.points)
def _evaluate_double(self, xi):
return self._do_evaluate(xi, 1.0)
def _evaluate_complex(self, xi):
return self._do_evaluate(xi, 1.0j)
@cython.boundscheck(False)
@cython.wraparound(False)
def _do_evaluate(self, double[:,::1] xi, double_or_complex dummy):
cdef double_or_complex[:,::1] values = self.values
cdef double_or_complex[:,::1] out
cdef double[:,::1] points = self.points
cdef int[:,::1] simplices = self.tri.simplices
cdef double c[NPY_MAXDIMS]
cdef double_or_complex fill_value
cdef int i, j, k, m, ndim, isimplex, inside, start, nvalues
cdef qhull.DelaunayInfo_t info
cdef double eps, eps_broad
ndim = xi.shape[1]
start = 0
fill_value = self.fill_value
qhull._get_delaunay_info(&info, self.tri, 1, 0)
out = np.zeros((xi.shape[0], self.values.shape[1]),
dtype=self.values.dtype)
nvalues = out.shape[1]
eps = np.finfo(np.double).eps * 100
eps_broad = sqrt(np.finfo(np.double).eps)
with nogil:
for i in xrange(xi.shape[0]):
# 1) Find the simplex
isimplex = qhull._find_simplex(&info, c,
&xi[0,0] + i*ndim,
&start, eps, eps_broad)
# 2) Linear barycentric interpolation
if isimplex == -1:
# don't extrapolate
for k in xrange(nvalues):
out[i,k] = fill_value
continue
for k in xrange(nvalues):
out[i,k] = 0
for j in xrange(ndim+1):
for k in xrange(nvalues):
m = simplices[isimplex,j]
out[i,k] = out[i,k] + c[j] * values[m,k]
return out实时公式预览
这个是我很关心的功能,也是Omni解决的很好的功能,预览文件使用的是离线的MathJax只要电脑够快,公式的渲染基本是实时的。(当然每次刷新都要重新渲染,这个是浏览器的固有缺陷,不是MathJax可以马上解决的,不过这种速度的预览我相当可以接受。)
\[\begin{array}{l} f(x+2h)-f(x-2h)-2\left(f(x+h)+f(x-h)\right)\\ =4 h \frac{d}{d x} f{\left (x \right )} + \frac{16h^{3}}{6} \frac{d^{3}}{d x^{3}} f{\left (x \right )}-2\left(2 h \frac{d}{d x} f{\left (x \right )} + \frac{2h^{3}}{6} \frac{d^{3}}{d x^{3}} f{\left (x \right )}\right) +\mathcal{O}\left(h^{5}\right)\\ = 2h^3 \frac{d^{3}}{d x^{3}} f{\left (x \right )} +\mathcal{O}\left(h^{5}\right) \end{array}\] \[\therefore \frac{d^{3}}{d x^{3}} f{\left (x \right )} =\frac{f(x+2h)-f(x-2h)-2\left(f(x+h)+f(x-h)\right)}{2 h^3} +\mathcal{O}\left(h^{2}\right)\] \[F(x) = \int_0^x f(x) \,\mathrm{d} x\]图片预览
这个也很重要,文件里插一个图看不到预览是相当不能接受的。支持远程文件的预览很正常,支持本地文件预览就麻烦一些。
远程文件:

本地文件:

可以看到,两种文件都得到了完美的支持。
表格支持
Markdown 渲染器支持,应该就没问题。
| Wang | Long | qi |
|---|---|---|
| How | & | Why |
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| A | B | C |
总结
通过Sublime Text和OmniMarkupPreviewer的合作,Markdown获得了很完美的支持,虽然有一些固有的技术障碍没有解决,不过在现有的组合中这是一个相当不错的解决方案了。如果你要经常编写Markdown文档的话,这是一个不错的解决方案。
下面是四个模板到处的实时预览的网页。
还没有好好弄弄这些模板,还有很多地方可以改进。啥时候有时间再改改。
